Glossary
Snowflake Datasets are built around two core concepts, entities and timeseries. Refer to our Unified Schema page for more details.
- Entities are concrete things or objects (e.g. a geography, a company, a mortgage application). All entities of a certain type are contained in Index Tables.
- Timeseries are abstract measures (ie. statistics) related to an entity and a date. Timeseries dates and values are included in Timeseries Tables.
Snowflake documentation includes key attributes for each of data product. Attributes can vary per table and timeseries. The attributes are defined as follows:
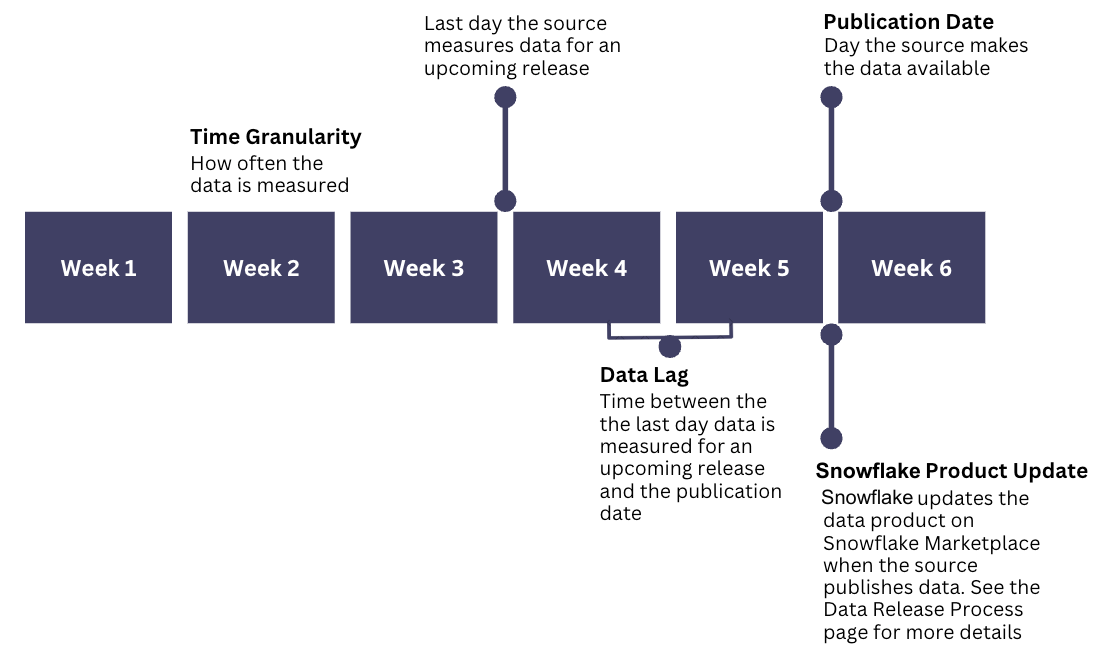
- Time Granularity: Level of detail, how often the data is measured
- Release Frequency: How often the Snowflake Data Product is updated. See Data Release Process for more details
- History: The earliest date included in the Snowflake Dataset. In some cases, Snowflake does not make all historical data available from a given source
- Entities Covered: The concrete things or objects (e.g. a company, a mortgage application) included in a Snowflake Data Product
- Geographic Coverage: The geographies covered (e.g. countries, states)
Other terms you will see throughout Snowflake documentation include:
- Snowflake Product Update: The day Snowflake adds new data from the underlying source to the Snowflake Data Product on Snowflake Marketplace
- Source: The publisher of the underlying data (e.g. government agencies, banks, give-to-get SEO applications, data aggregators)
- Source Schedule: How frequently the source updates data
- Snowflake Monitor: How often Snowflake monitors the underlying data source for new releases. See Data Release Process for more details
- Data Lag: The time between the last day the source measures data for an upcoming release and the publication date
- Publication Date: The day the underlying source makes new data available for consumption